How To Check For Disk Space On Mac With Osx
Each version of OS X in recent years has been more efficient and often sheds space after installation rather than demanding more. However, Thom Vagt found the opposite: an upgrade led to less reported remaining space. On my late 2013 model MBP which was running Yosemite 10.10.5, my available disk space went from 230GB of free space to 183GB. I have run disk utility and it tells me all is fine with the SSD 1TB disk.
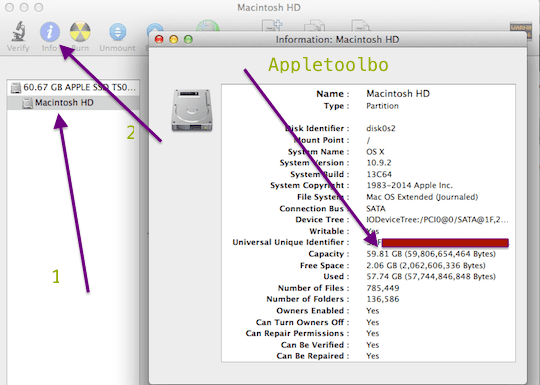
I’ve seen similar problems at times with my various Macs, and so have many users. You should pinpoint where the free-space reporting error is first, however. The About This Mac window reveals space use on drives in a graphical display. Is it accurate? OS X reports remaining storage in multiple ways: • Select > About This Mac, and the Storage tab reveals all attached drives, along with breakdowns by coarse file type for bootable (“blessed”) volumes.
Checking your hard disk space is easy on a Mac, and can let you know how much space you have left to install new games or programs, store media or download large files. A window displaying the current OS X version and some other basic information about the machine will come up. If you8 wonder how to check disk space on Mac using the Movavi Software, it is very easy. You just need to download the software from their website and installing it by going through the screen instructions. Once the scanning is done with, Mac Cleaner will show the results on the right hand.
• In the Finder, select a volume then choose File > Get Info (Command-I). The General area shows data used and remaining. The bottom of every Finder window with the status bar enabled ( View >Convert handwriting to text ipad. Show Status Bar) shows remaining storage on the volume that the window represents, too. How to create a data table in excel for mac. • Via Terminal, type df -h and you’ll get a human-readable summary by volume in columns marked Used, Avail, and Capacity (as a percentage). (The Gi or Ti refers to gibibytes and tebibytes, base 2 units for a billion and trillion bytes instead of the base 10 gigabytes and terabytes.) The command-line df program tells you what the low-level system thinks about storage usage on mounted drives.
If these don’t agree, it’s likely a Spotlight error. Apple relies on Spotlight to mark and calculate remaining storage on the startup volume. You can delete the Spotlight index and rebuild it by following these steps: • Open the Spotlight preference pane. • Click the Privacy tab. • Drag the startup volume into the Privacy window. • Click OK at the warning, and the Spotlight index is deleted. • Select your startup volume in the privacy list, and click the - (minus) button.
That restarts indexing. This should reset your storage. Removing the startup drive from Spotlight indexing can reset a wonky problem with the display of remaining storage on that drive. If all the numbers agree, it could be temporary caches, which in previous releases of OS X before El Capitan, I’ve sometimes seen grow to 30GB to 50GB on one of my Macs. Restarting clears the cache and regains that storage space, though the same problem can recur over time. Ask Mac 911 We’re always looking for problems to solve!
Email yours to including screen captures as appropriate. Mac 911 cannot reply to email with troubleshooting advice nor can we publish answers to every question. Update: This article originally swapped base 2 and 10 units when referring to storage measurements.